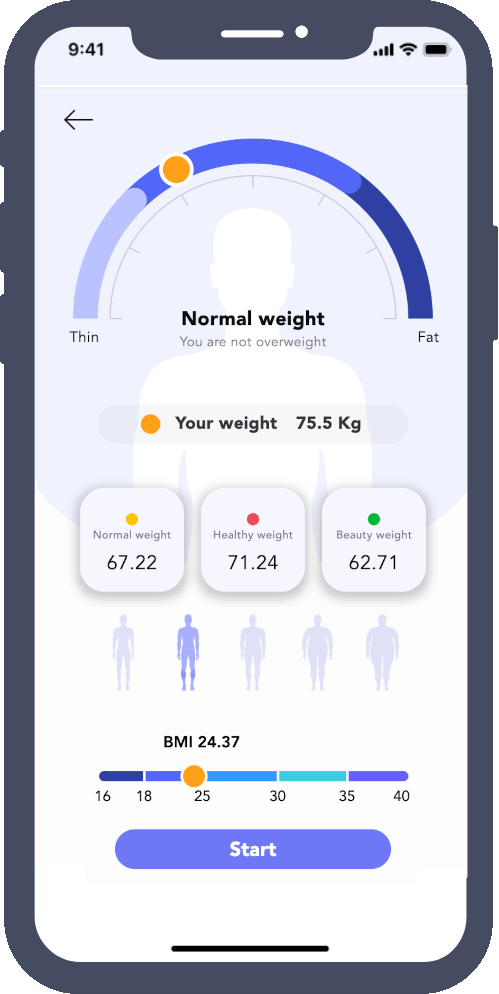
Obesity and related disorders such as diabetes are among the major concerns in today’s societies. These conditions are caused by multiple factors, including excessive consumption of energy-dense diets and reduced physical activity1.
Several studies have revealed that intestinal microbiota holds significant therapeutic potential in addressing obesity2. It has also been observed that butyrate (a regulator of intestinal microbiota) can help regulate body weight, in part by inhibiting food intake3.
This raises an important question: how can we modulate the gut microbiota?
According to research, two key factors—physical activity and the use of prebiotics—can greatly aid in modulating the gut microbiota. Engaging in 90 to 180 minutes of moderate to high-intensity aerobic exercise per week has been shown to increase butyrate production4. This is roughly equivalent to 15 to 20 minutes of moderate-intensity walking each day.
Common sources of prebiotics include garlic, onions, apples, cocoa, bananas, flaxseed, barley, oats, wheat bran, asparagus, chicory, burdock, artichokes, and leeks.
References:
- Yu, C., Liu, S., Chen, L., Shen, J., Niu, Y., Wang, T., Zhang, W., & Fu, L. (2019). Effect of exercise and butyrate supplementation on microbiota composition and lipid metabolism. Journal of Endocrinology, 243(2), 125–135.
- Bouter, K. E., van Raalte, D. H., Groen, A. K., & Nieuwdorp, M. (2017). Role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis of obesity and obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. Gastroenterology, 152(7), 1671–1678. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.048
- Liu, X., Niu, Y., Yuan, H., Huang, J., & Fu, L. (2015). AMPK binds to Sestrins and mediates the effect of exercise to increase insulin sensitivity through autophagy. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 64(5), 658–665.
- Allen, J. M., Mailing, L. J., Niemiro, G. M., Moore, R., Cook, M. D., White, B. A., ... & Woods, J. A. (2018). Exercise alters gut microbiota composition and function in lean and obese humans. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 50(4), 747–757.